|
Pressure Exerted by Liquids in simple Experiments:
|
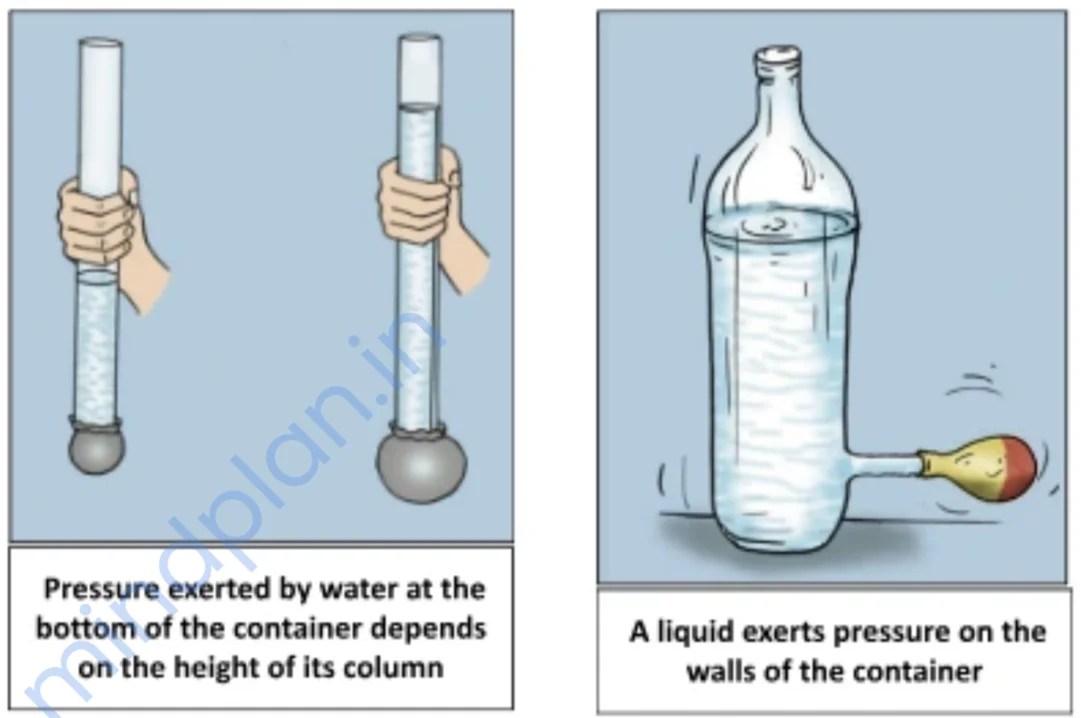
- In experiments involving rubber sheets covering a container, it’s observed that as water is poured into the container, the rubber sheet bulges out.
- The greater the volume or height of the water, the more the rubber bulges, indicating that liquids exert pressure not only on the base but also on the walls of their container.
- By drilling holes into a bottle, we observe that water flows out of all the holes, and if the holes are at the same height, the water will fall at the same distance from the bottle.
- This experiment indicates that liquids exert uniform pressure at the same depth or height on the walls of their container.

|
|
Fluid Dynamics in Action: Pressure Exerted by Gases in everyday Experiences:
|
- When inflating a balloon, air fills up the available space. If the balloon’s mouth isn’t sealed, the air rushes out when released, demonstrating that the air inside was exerting pressure on the inner walls of the balloon.
- If the balloon has holes, it won’t inflate because the air would escape, further illustrating that gases exert pressure on their container’s walls.
- In the context of a bicycle tire, if there’s a puncture, air rushes out.
- This shows that the air inside was exerting pressure on the inner walls of the tube.

|


